ADAPTER
The Adapter design pattern is a structural design pattern that allows objects with incompatible interfaces to work together. It acts as a bridge between two incompatible interfaces, converting the interface of one class into another interface that clients expect. This pattern is useful when you want to reuse an existing class but its interface is not compatible with the rest of the system.
In the provided example, let’s consider a scenario where we have two payment gateways: Razorpay and CCAvenue. Each gateway has its own specific interface for processing payments, which is incompatible with our client code. The goal is to provide a unified interface to our clients, so they can use any payment gateway interchangeably without worrying about the specific implementation details.
To achieve this, we utilize the Adapter design pattern. Here’s how it works:
OVERVIEW (UML)
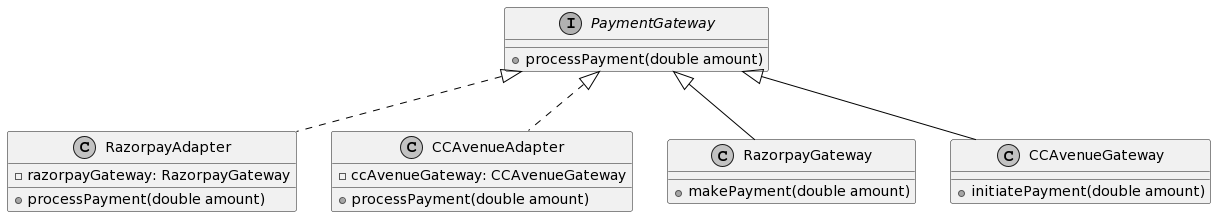 Created using PlantUML.
Created using PlantUML.
PaymentGateway is associated with RazorpayAdapter and CCAvenueAdapter using a solid line with an arrowhead. This association represents that both RazorpayAdapter and CCAvenueAdapter implement the PaymentGateway interface.
PaymentGateway is associated with RazorpayGateway and CCAvenueGateway using a solid line with an arrowhead. This association represents that both RazorpayGateway and CCAvenueGateway provide an implementation for the PaymentGateway interface.
CODE WALKTHROUGH
INTERFACES
PaymentGateway (Target Interface): This interface represents the common interface that our clients expect. It declares the processPayment method, which is used to process payments.
1
2
3
4
5
6
package com.designpattern;
//PaymentGateway interface represents the target interface that our clients expect.
public interface PaymentGateway {
void processPayment(double amount);
}
INCOMPATIBLE CLASSES
RAZORPAYGATEWAY (ADAPTEE)
This class represents the Razorpay payment gateway. It has its own specific interface, makePayment, which is incompatible with our PaymentGateway interface
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
package com.thirdparty;
//RazorpayGateway is an example of an incompatible class that has its own specific interface.
public class RazorpayGateway {
public void makePayment(double amount) {
System.out.println("Processing payment via Razorpay: " + amount);
}
}
CCAVENUEGATEWAY (ADAPTEE)
This class represents the CCAvenue payment gateway. It also has its own specific interface, initiatePayment, which is incompatible with our PaymentGateway interface
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
package com.thirdparty;
//CCAvenueGateway is another incompatible class with its own specific interface.
public class CCAvenueGateway {
public void initiatePayment(double amount) {
System.out.println("Initiating payment via CCAvenue: " + amount);
}
}
ADAPTERS
RAZORPAYADAPTER
This adapter class implements the PaymentGateway interface. It internally holds an instance of RazorpayGateway and adapts its makePayment method to the processPayment method defined in the PaymentGateway interface
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
package com.designpattern;
import com.thirdparty.RazorpayGateway;
public class RazorpayAdapter implements PaymentGateway {
private RazorpayGateway razorpayGateway;
public RazorpayAdapter(RazorpayGateway razorpayGateway) {
this.razorpayGateway = razorpayGateway;
}
@Override
public void processPayment(double amount) {
razorpayGateway.makePayment(amount);
}
}
CCAVENUEADAPTER
This adapter class also implements the PaymentGateway interface. It internally holds an instance of CCAvenueGateway and adapts its initiatePayment method to the processPayment method defined in the PaymentGateway interface. Client:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
package com.designpattern;
import com.thirdparty.CCAvenueGateway;
public class CCAvenueAdapter implements PaymentGateway{
CCAvenueGateway ccAvenueGateway;
public CCAvenueAdapter(CCAvenueGateway ccAvenueGateway) {
this.ccAvenueGateway = new CCAvenueGateway();
}
@Override
public void processPayment(double amount) {
ccAvenueGateway.initiatePayment(amount);
}
}
APP (CLIENT)
This is our client code that utilizes the PaymentGateway interface. It is unaware of the specific payment gateways or their implementations. It creates instances of the adapters (RazorpayAdapter and CCAvenueAdapter) and uses them interchangeably to process payments through the unified PaymentGateway interface
By using the adapters, we can seamlessly integrate the incompatible payment gateways into our client code. The adapters provide a common interface (PaymentGateway) that clients can use, regardless of the underlying payment gateway implementation. This allows for flexibility and extensibility, as we can easily add or swap out payment gateways without affecting the client code.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
package com.demo;
import com.designpattern.CCAvenueAdapter;
import com.designpattern.PaymentGateway;
import com.designpattern.RazorpayAdapter;
import com.thirdparty.CCAvenueGateway;
import com.thirdparty.RazorpayGateway;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PaymentGateway gateway1 = new RazorpayAdapter(new RazorpayGateway());
gateway1.processPayment(1000);
PaymentGateway gateway2 = new CCAvenueAdapter(new CCAvenueGateway());
gateway2.processPayment(2000);
}
}
OUTPUT
1
2
Processing payment via Razorpay: 1000.0
Initiating payment via CCAvenue: 2000.0
