STRATEGY
The Strategy design is a behavioral design pattern that allows us to define different strategies (or ways) to solve a problem and switch between them easily. It helps us encapsulate each strategy into its own class and use them interchangeably. This way, we can change the strategy at runtime without changing the overall code structure.
We can consider using strategy design pattern when there are different ways of doing similar work. For example, to sort a given array, we can use multiple algorithms like quick sort, merge sort etc. Another example is for payment - we can do our payment using multiple ways like debit card, paypal etc. In this blog, we will look at navigation example, which has different ways to calculate the distance/time from location A to B depending on the Navigation strategy - Car, Bike or Walk.
OVERVIEW (UML)
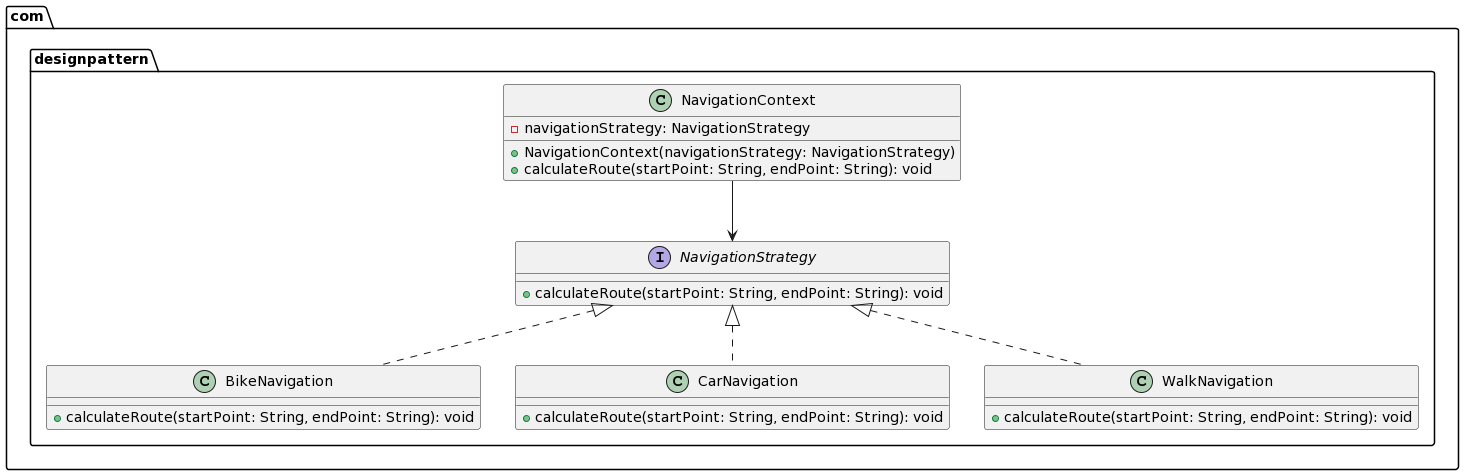 Created using PlantUML.
Created using PlantUML.
CODE WALKTHROUGH
NAVIGATION STRATEGY (INTERFACE)
Represents the behavior of different navigation modes.
1
2
3
4
5
package com.designpattern;
public interface NavigationStrategy {
void calculateRoute(String startPoint, String endPoint);
}
NAVIGATION STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATIONS (CONCRETE CLASSES)
Concrete classes that implement the NavigationStrategy interface for different modes of transportation.
CAR NAVIGATION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
package com.designpattern;
public class CarNavigation implements NavigationStrategy{
public void calculateRoute(String startPoint, String endPoint) {
// Implementation of car navigation logic using Google Maps API
System.out.println("Calculating car route from " + startPoint + " to " + endPoint);
// Additional car navigation code...
}
}
BIKE NAVIGATION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
package com.designpattern;
public class BikeNavigation implements NavigationStrategy {
public void calculateRoute(String startPoint, String endPoint) {
// Implementation of bike navigation logic using Google Maps API
System.out.println("Calculating bike route from " + startPoint + " to " + endPoint);
// Additional bike navigation code...
}
}
WALK NAVIGATION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
package com.designpattern;
public class WalkNavigation implements NavigationStrategy {
public void calculateRoute(String startPoint, String endPoint) {
// Implementation of walking navigation logic using Google Maps API
System.out.println("Calculating walking route from " + startPoint + " to " + endPoint);
// Additional walking navigation code...
}
}
NAVIGATION CONTEXT (HAS-A NAVIGATION STRATEGY)
NavigationContext will use the chosen navigation strategy. In the NavigationContext class, we have a reference to the NavigationStrategy interface called navigationStrategy. The setNavigationStrategy method allows us to dynamically set the desired navigation mode at runtime. The calculateRoute method delegates the route calculation to the chosen strategy.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
package com.designpattern;
public class NavigationContext {
NavigationStrategy navigationStrategy;
public NavigationContext(NavigationStrategy navigationStrategy) {
this.navigationStrategy = navigationStrategy;
}
public void calculateRoute(String startPoint, String endPoint) {
navigationStrategy.calculateRoute(startPoint, endPoint);
}
}
CLIENT
By using the Strategy design pattern, we can easily switch between different navigation modes without changing the client code. This allows us to calculate routes using different transportation methods based on the user’s preference or specific requirements.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
package com.demo;
import com.designpattern.BikeNavigation;
import com.designpattern.CarNavigation;
import com.designpattern.NavigationContext;
import com.designpattern.WalkNavigation;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String startPoint = "A";
String endPoint = "B";
// Create a NavigationContext with the car navigation strategy
NavigationContext carNavigationContext = new NavigationContext(new CarNavigation());
carNavigationContext.calculateRoute(startPoint, endPoint);
// Create a NavigationContext with the bike navigation strategy
NavigationContext bikeNavigationContext = new NavigationContext(new BikeNavigation());
bikeNavigationContext.calculateRoute(startPoint, endPoint);
// Create a NavigationContext with the walking navigation strategy
NavigationContext walkNavigationContext = new NavigationContext(new WalkNavigation());
walkNavigationContext.calculateRoute(startPoint, endPoint);
}
}
OUTPUT
1
2
3
Calculating car route from A to B
Calculating bike route from A to B
Calculating walking route from A to B
