Problem Description
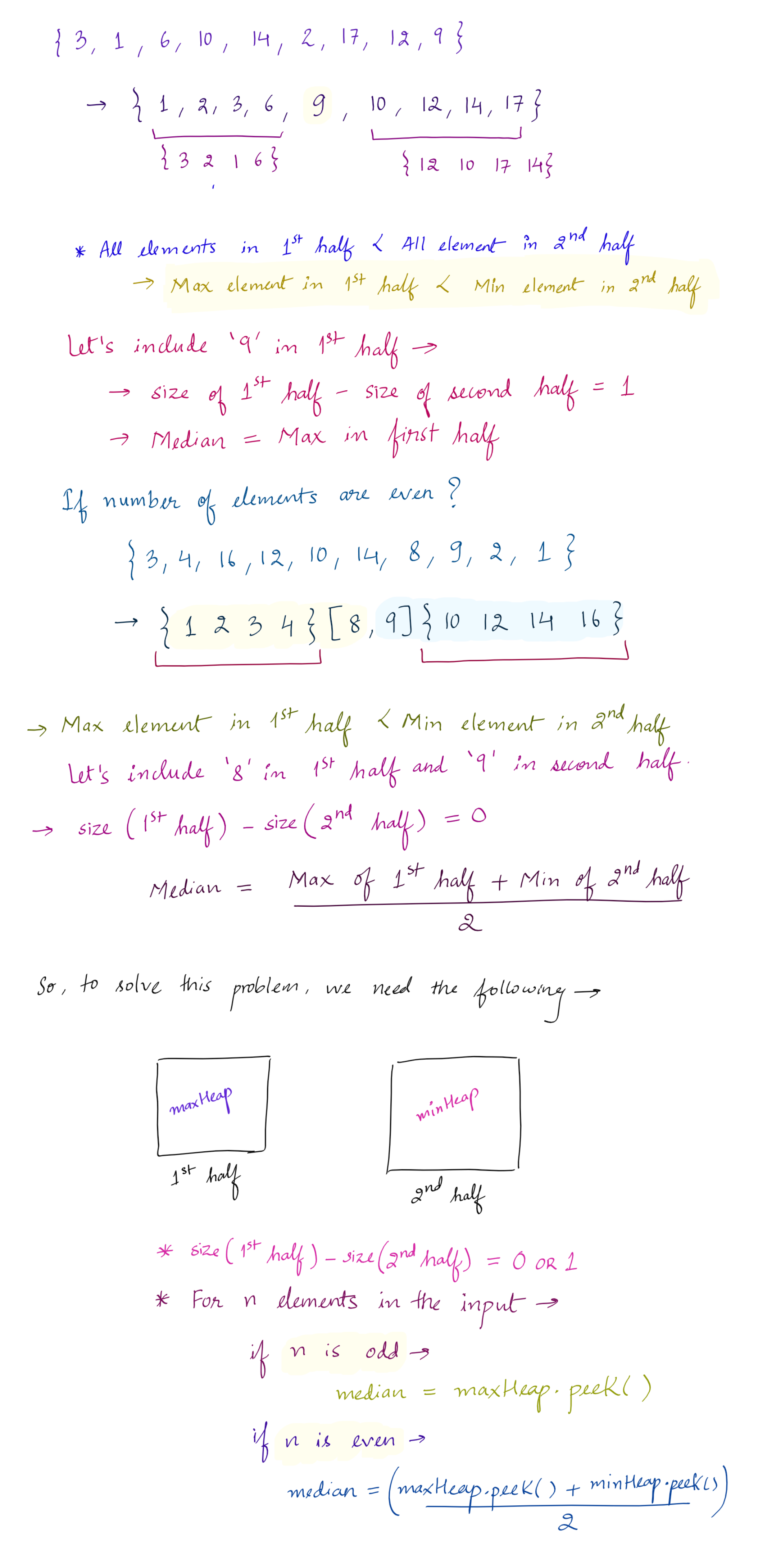
The median is the middle value in an ordered integer list. If the size of the list is even, there is no middle value and the median is the mean of the two middle values.
- For example, for arr = [2,3,4], the median is 3.
- For example, for arr = [2,3], the median is (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
Implement the MedianFinder class:
- MedianFinder() initializes the MedianFinder object.
- void addNum(int num) adds the integer num from the data stream to the data structure.
- double findMedian() returns the median of all elements so far. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
class MedianFinder {
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap; //first half
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap; //second half
public MedianFinder() {
maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
}
public void addNum(int num) {
//if both are empty, add to maxHeap (because we want to ensure size(maxHeap)-size(minHeap) is 0 or 1)
if(minHeap.size() == 0 && maxHeap.size() == 0){
maxHeap.add(num);
return;
}
int max = maxHeap.peek();
//if the current number is less than max in left half, add to maxHeap
if(num > max){
minHeap.add(num);
//else add to minHeap (second Half)
}else{
maxHeap.add(num);
}
//left half has 1 extra number, so move the largest on to minHeap
//we want to ensure that all numbers in second half is more than all numbers in left half
if(maxHeap.size() - minHeap.size() > 1){
minHeap.add(maxHeap.poll());
return;
}
//if second half has more numbers, move the minimum in second half to first half
if(maxHeap.size() - minHeap.size() < 0){
maxHeap.add(minHeap.poll());
return;
}
}
public double findMedian() {
int size = minHeap.size() + maxHeap.size();
if(size%2 != 0){
return (double)maxHeap.peek();
}else{
return ((double)maxHeap.peek()+(double)minHeap.peek())/2.0;
}
}
}
