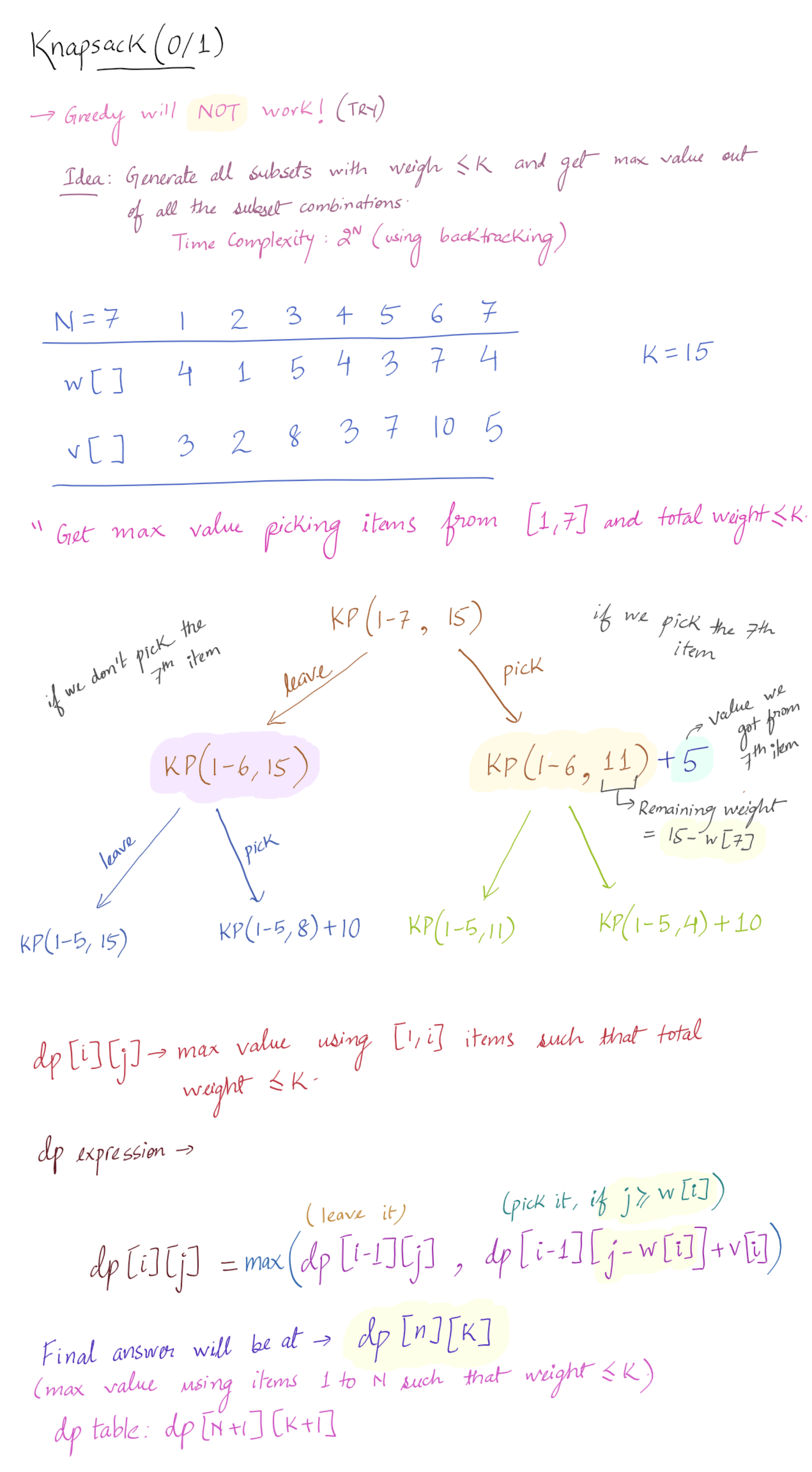
Problem Description
Given weights and values of n items, put these items in a knapsack of capacity W to get the maximum total value in the knapsack. In other words, given two integer arrays val[0..n-1] and wt[0..n-1] which represent values and weights associated with n items respectively. Also given an integer W which represents knapsack capacity, find out the maximum value subset of val[] such that sum of the weights of this subset is smaller than or equal to W. You cannot break an item, either pick the complete item or don’t pick it (0-1 property).
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
class Solution
{
//Function to return max value that can be put in knapsack of capacity W.
static int knapSack(int k, int w[], int v[], int n)
{
//dp state:: get max value by choosing items [1,i] such that the total weight is <= j
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][k+1];
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++){
Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);
}
KP(w, v, n, k, dp);
return dp[n][k];
}
public static int KP(int[] w, int[] v, int i, int j, int[][] dp){
//no items to pick
if(i == 0){ // j == 0 is not required, because we are later checking if j>=w[i-1]
return 0;
}
if(dp[i][j] == -1){
//leave
int x = KP(w, v, i-1, j, dp);
//pick
if(j >= w[i-1]){
x = Math.max(x, KP(w, v, i-1, j-w[i-1], dp) + v[i-1]);
}
dp[i][j] = x;
}
return dp[i][j];
}
}
ITERATIVE SOLUTION
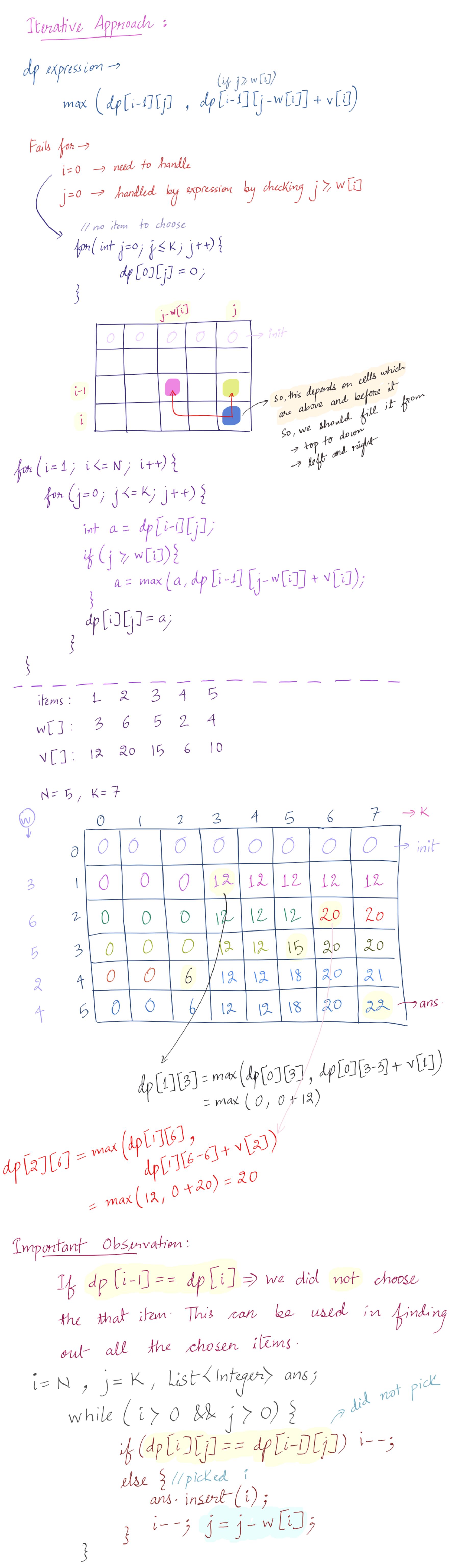
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
class Solution
{
//Function to return max value that can be put in knapsack of capacity W.
static int knapSack(int k, int w[], int v[], int n)
{
//dp table
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][k+1];
//i=0 => no item selected, so value will be 0, which is already there by default.
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<=k; j++){
//leave
int x = dp[i-1][j];
//pick
if(j >= w[i-1])
x = Math.max(x, dp[i-1][j-w[i-1]] + v[i-1]);
dp[i][j] = x;
}
}
return dp[n][k];
}
}
SPACE OPTIMIZATION
At any given time, we just need two rows, since we are looking into the previous row and updating the current row. We can use mod by 2 to just make use of 2 rows.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
class Solution
{
static int knapSack(int k, int w[], int v[], int n)
{
int[][] dp = new int[2][k+1];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<=k; j++){
//leave
int x = dp[(i-1)%2][j];
//pick
if(j >= w[i-1])
x = Math.max(x, dp[(i-1)%2][j-w[i-1]] + v[i-1]);
dp[i%2][j] = x;
}
}
return dp[n%2][k];
}
}
