Problem Description
Given a positive integer n, find the smallest integer which has exactly the same digits existing in the integer n and is greater in value than n. If no such positive integer exists, return -1.
Note that the returned integer should fit in 32-bit integer, if there is a valid answer but it does not fit in 32-bit integer, return -1.
Solution
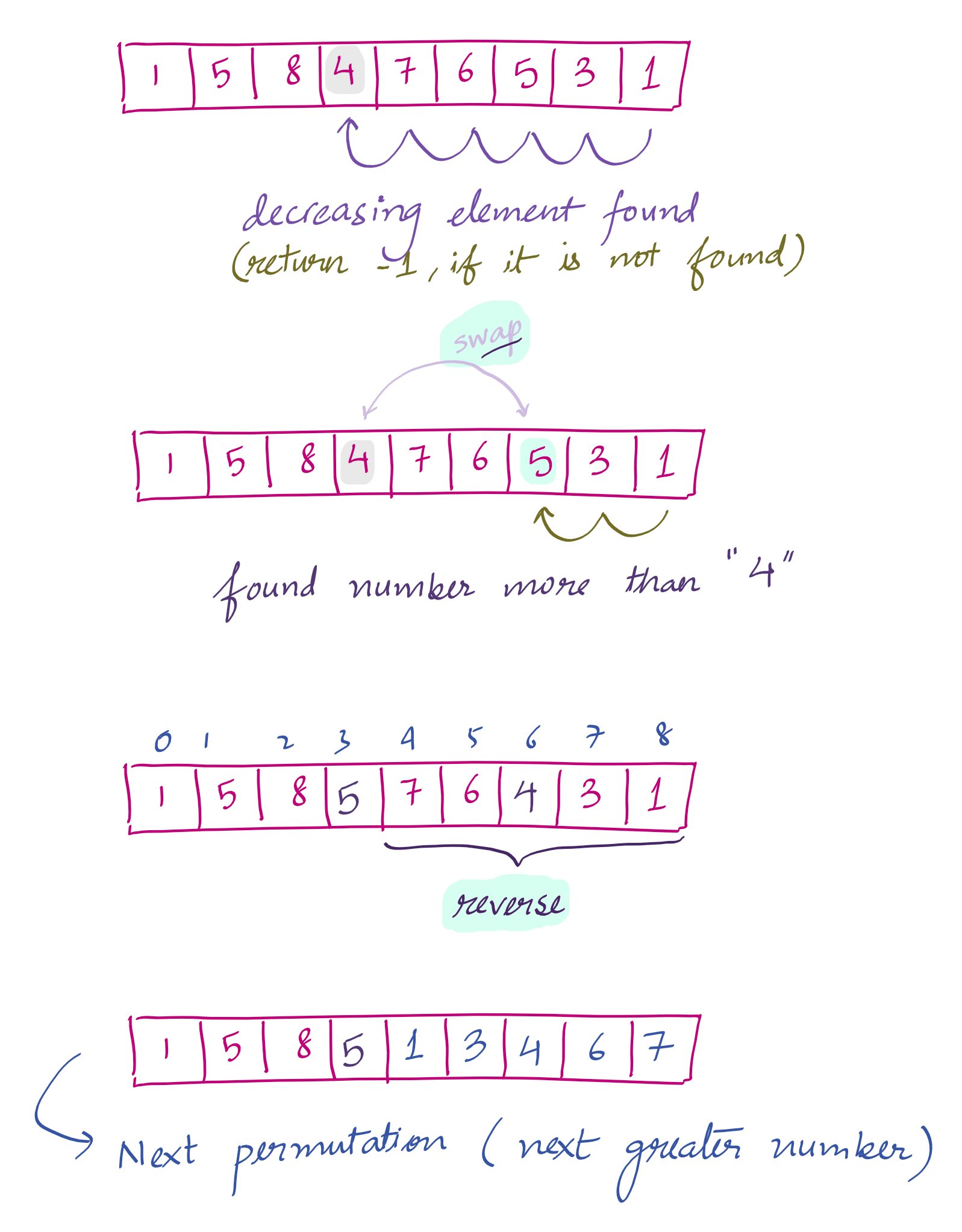
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
class Solution {
public int nextGreaterElement(int n) {
int[] num = new int[String.valueOf(n).length()];
int temp = n;
for(int i=num.length-1; i>=0; i--){
int digit = temp%10;
temp = temp/10;
num[i] = digit;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));
//Decreasing element
int a = -1;
for(int i=num.length-2; i>=0; i--){
if(num[i] < num[i+1]){
a = i;
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Decreaing index: " + a);
if(a == -1) return -1;
//First element more than num[a] from right
int b = -1;
for(int i=num.length-1; i>a; i--){
if(num[i] > num[a]){
b = i;
break;
}
}
swap(a, b, num);
reverseFrom(a+1, num);
return convert(num);
}
public int convert(int[] arr){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){
sb.append(arr[i]+"");
}
try{
return Integer.parseInt(sb.toString());
}catch(Exception e){
return -1;
}
}
public void reverseFrom(int i, int[] arr){
int start=i;
int end=arr.length-1;
while(start<end){
swap(start, end, arr);
start++;
end--;
}
}
public void swap(int i, int j, int[] arr){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
