PROBLEM DESCRIPTION
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
SOLUTION
APPROACH 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
//get size of linked list
int size = getSize(head);
//if size of list is 0, return head
if(size == 0) return head;
//else, update k to k%size since after n rotations we'll get the same list (n is the number of nodes)
k=k%size;
//if k is now 0, means no rotation needed
if(k == 0) return head;
//reverse the list
head = reverse(head);
//reverse first k nodes
head = reverseK(head, k);
//move to kth node
ListNode temp = head;
for(int i=1; i<k; i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
//next of kth node will be reverse of remaining list
temp.next = reverse(temp.next);
return head;
}
//get the size of linked list
public int getSize(ListNode head){
int s = 0;
while(head != null){
s++;
head=head.next;
}
return s;
}
//reverse first K nodes of the linked list
public ListNode reverseK(ListNode head, int k){
ListNode h1= head;
ListNode h2= null;
ListNode t = head;
ListNode h3 = head;
while(k>0 && h1 != null){
h1 = h1.next;
t.next = h2;
h2 = t;
t = h1;
k--;
}
h3.next = h1;
return h2;
}
//reverse complete linked list
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
ListNode h1= head;
ListNode h2= null;
ListNode t = head;
while(h1 != null){
h1 = h1.next;
t.next = h2;
h2 = t;
t = h1;
}
return h2;
}
}
ANOTHER WAY TO CODE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
// Get the total number of nodes in the linked list.
int nodes = getNodeCount(head);
// Check for edge cases where no rotation is needed.
// Make sure to check k%nodes at the last (k can be zero)
if(k == 0 || head == null || nodes == 0 || k % nodes == 0) {
return head;
}
// Calculate the effective rotation by taking the remainder.
k = k % nodes;
// Reverse the entire linked list.
head = reverseList(head);
// Move a pointer to the k-th node from the start.
ListNode t = head;
for(int i = 1; i < k; i++) {
t = t.next;
}
// Create two pointers: h1 for the rotated head, and h2 for the second part.
ListNode h1 = head;
ListNode h2 = t.next;
// Break the list into two parts by disconnecting the end of the first part.
t.next = null;
// Reverse both parts separately.
h1 = reverseList(h1);
h2 = reverseList(h2);
// Connect the rotated head with the second part.
// the head pointer is actually the tail of h1 now, so we can use that.
head.next = h2;
// Return the rotated linked list.
return h1;
}
// Function to count the number of nodes in the linked list.
public int getNodeCount(ListNode head) {
int count = 0;
ListNode t = head;
while(t != null) {
count++;
t = t.next;
}
return count;
}
// Function to reverse a linked list.
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode h2 = null; // Initialize a new head for the reversed list.
ListNode current = head;
// Traverse the original list, changing the next pointers to reverse the connections.
while(current != null) {
ListNode next = current.next; // Store the next node temporarily.
// Reverse the pointer to the previous node.
current.next = h2;
h2 = current; // Move the new head pointer to the current node.
current = next; // Move to the next node.
}
return h2; // Return the new head of the reversed list.
}
}
BEST SOLUTION
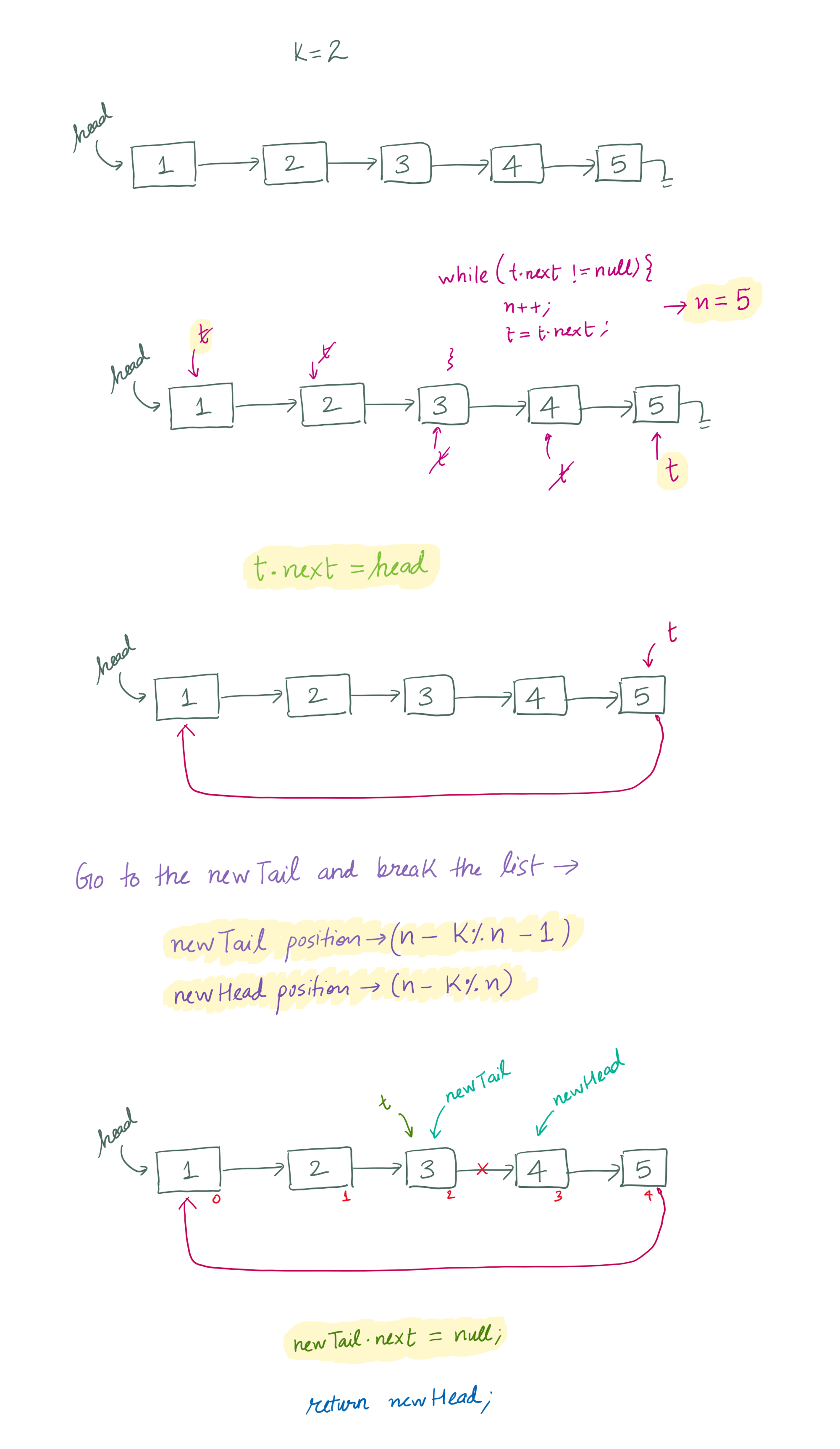
First, we count the total number of nodes in the list. We then create a circular loop by connecting the last node to the first node. To determine where to break the loop for rotation, we calculate (n - k % n - 1) steps, where ‘n’ is the total number of nodes. This brings the pointer to the node just before the new rotated head. The next node becomes the new head, and the previous node is disconnected to finalize the rotation.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
// Check for edge cases where rotation is not needed.
if (head == null || head.next == null || k == 0) {
return head;
}
ListNode t = head;
int n = 1; // Initialize the count of nodes.
while (t.next != null) {
n++;
t = t.next;
}
t.next = head; // Close the ring by connecting the tail to the head.
// Determine where to break the list for rotation.
// The tail of the rotated list will be the (n - k % n - 1)-th node.
// The new head of the rotated list will be the (n - k % n)-th node.
// For example, in a list of 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5:
// If n = 5 (number of nodes) and k = 2 (rotation count),
// The tail will be the (5 - 2 % 5 - 1) = 2nd node (3). -- 0 index
// The new head will be the (5 - 2 % 5) = 3rd node (4). -- 0 index
// So, we break the list after the 2nd node (3).
for (int i = 0; i <= n - k % n - 1; i++) {
t = t.next;
}
ListNode newHead = t.next; // Get the new head of the rotated list.
t.next = null; // Break the list at the rotation point.
return newHead; // Return the rotated linked list.
}
}
